Beginning with the first beta of iOS 16.4, Apple is rolling out support for 5G Standalone mode (5G SA). With supported 5G networks, this will allow you much faster data speeds than ever before, but it could come at a cost. Here’s a rundown of what 5G Standalone mode does and how you can take advantage of it on your iPhone.
How to Turn On 5G Standalone Mode on iOS 16.4
If you want to make the most of the data speeds your cellular provider offers you, that means switching over to 5G Standalone. Unfortunately, this is a gradual rollout: as of this writing, the only U.S. carrier to support 5G SA is T-Mobile.
Once you’ve got iOS 16.4 installed on your iPhone, you can flip the switch on 5G Standalone in Settings.
- Go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Voice & Data.
- Toggle on 5G Standalone, if available.
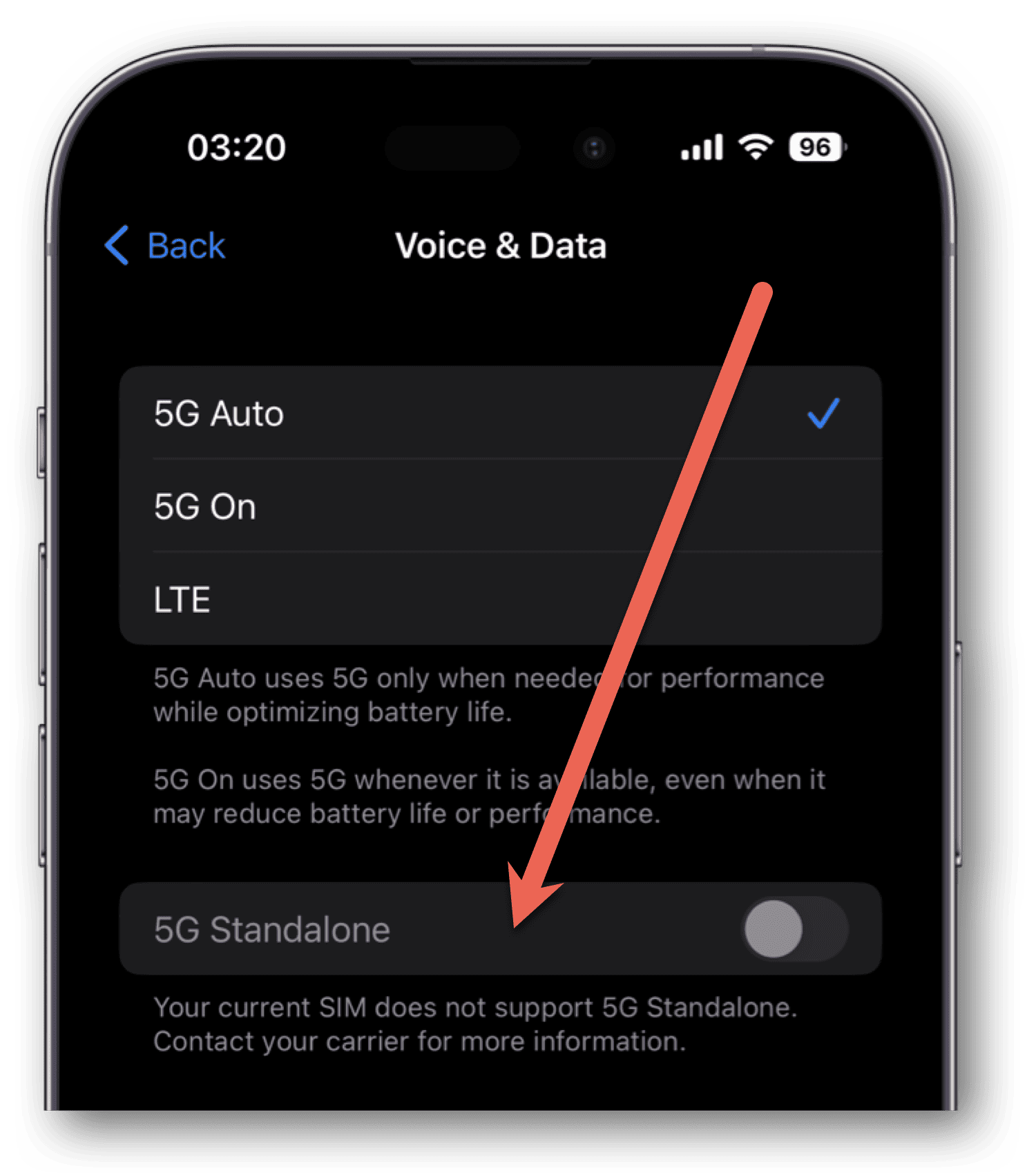
Note what the other options on this page mean for your device.
- 5G Auto will only use the 5G network when it’s going to offer you better performance while also preserving your battery life.
- 5G On will utilize 5G connections whenever available, even if doing so might reduce battery life or performance.
- LTE means your device ignores the 5G network altogether, using only LTE connectivity.
The Nuts and Bolts of 5G Standalone Mode
So, now you’re probably asking just what 5G Standalone mode is in the first place. In a nutshell, 5G Standalone mode allows your device to enjoy even faster and more reliable data connections than ever before.
The reason is this: when cell providers first rolled out 5G, they maintained compatibility with the older LTE cellular networks. Carriers continued to use the existing infrastructure of the 4G/LTE network, which was never built with the potential of 5G speeds or demands in mind. This mode is also known as 5G Non-Standalone, or 5G NSA.
Preparing for Tomorrow’s Problems Today
That’s not to say 5G SA is absolutely necessary now. According to tech journalist and analyst Peter Cohen, “many international carriers are still getting 5G NSA networks up and running and built out before they transition their network cores.”
They’ve been slow to transition their network cores because, frankly, there isn’t a lot of need for them to do so. 4G LTE is performant enough and gives them enough growth runway that 5G SA is a tomorrow problem, not a today problem.
In migrating to a 5G Standalone network, carriers need to build out an entirely new cloud-native 5G core network. This, as it’s executed, turns on the full potential of a 5G cellular network.
In essence, the existing backbone of the cellular networks won’t be able to support devices hitting the speeds 5G supports as more high-speed devices come online. Nor will they be able to handle the ultra reliable low latency communications needed for future technologies such as the metaverse and widespread autonomous driving applications. As the carriers roll out standalone 5G networks, that changes.
What Does 5G SA Give Me?
In the U.S., T-Mobile is currently the only cellular carrier to officially offer 5G SA service. The carrier began touting the network in November 2022, saying it provides much, much faster data transfer speeds than other networks.
In fact, T-Mobile’s standalone 5G network offers speeds that rival many fiber internet offerings: up to 3Gbps. It accomplishes this by aggregating data speeds across three 5G mid-band channels. Until now, the only devices that could take advantage of this speed were a few flagship Samsung devices.
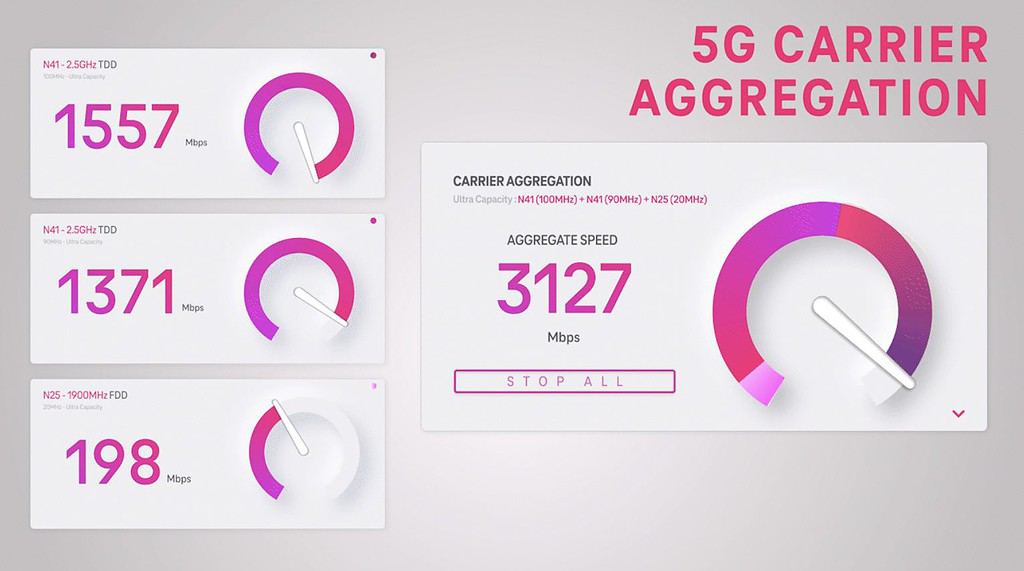
In the first iOS 16.4 beta, a new toggle appears for 5G standalone. It only works, however, for T-Mobile customers in the U.S. For those lucky few, it’s actually turned on by default.
Of course, T-Mobile hasn’t officially announced support for the feature on iPhone at all, much less which devices support it. There is a possibility it will only be available to iPhone 14 owners, but that remains to be seen.
