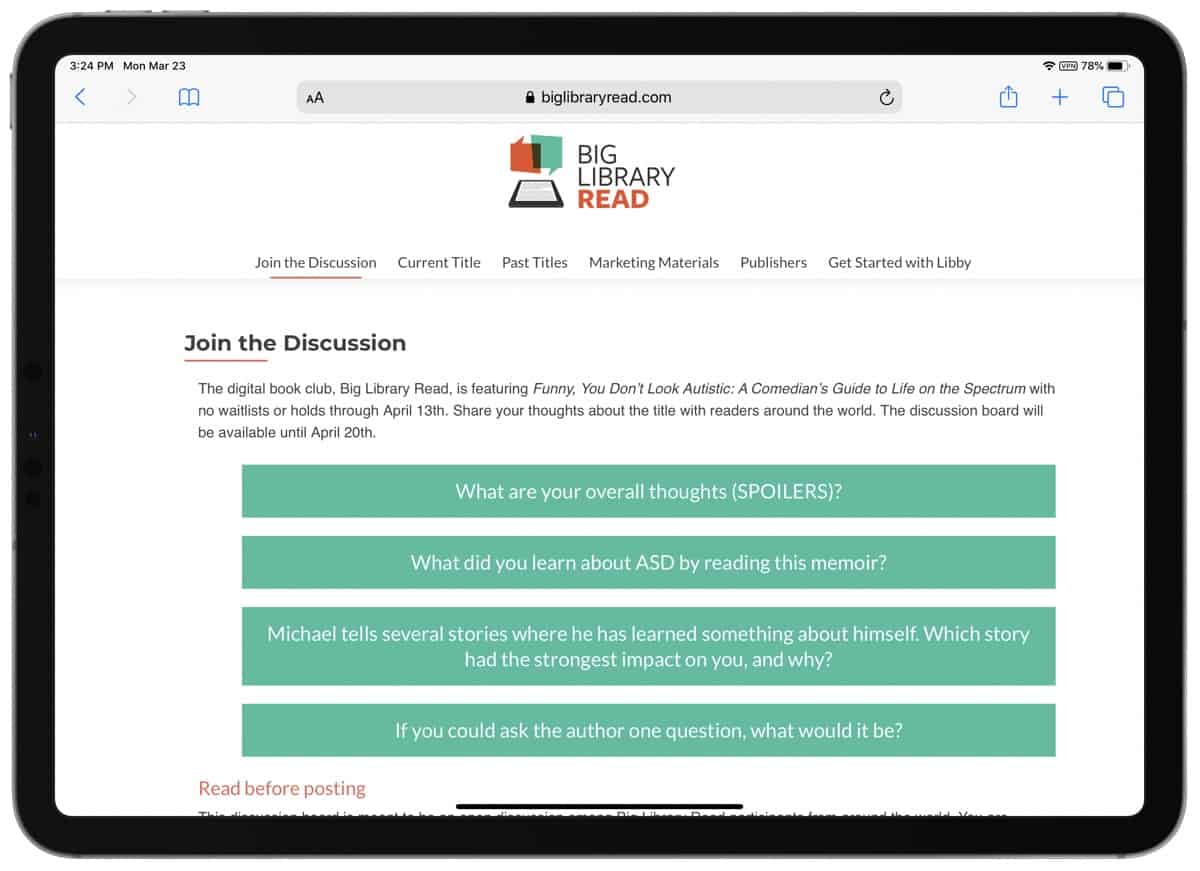
Big Library Read is an online book club from OverDrive. It connects readers from around the world with one eBook at a time and offers a place to share your thoughts, comments, and questions of the book with other readers.
This round’s title is Funny, You Don’t Look Autistic, a memoir written by stand-up comedian Michael McCreary who shares his experiences of living on the spectrum and dealing with trying situations as someone who doesn’t “look” autistic.
I think it’s a great idea, and be sure to download the Libby app so you can borrow books from your local library.